Tubulin
May 2022
Tubulin
Tubulins are heterodimeric and globular proteins. Their subunits (α and β tubulins) are the main building blocks of microtubules – a major component of all eukaryotic cells. Tubulins, therefore, play a critical role in multiple cellular processes, such as cell division and intracellular transport, which makes them an important target for cancer therapy.
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes are known anticancer agents that inhibit mitosis by targeting tubulins. However, their wider clinical application has been restricted by drug resistance and toxicity and especially due to their complex chemical structures (difficult and costly to synthesize). Scientists are currently working on novel strategies to overcome those limitations and improve the clinical efficacy of anti-tubulin drugs.
Following the indications of the fragment-based approach, Swiss and Italian researchers have developed a novel small-molecule tubulin inhibitor – Todalam – with a unique mechanism of action.
They performed a crystallographic fragment screening and identified a novel binding site called sID βαII, located at the βTub1-αTub2 interdimer interface of the T2R-TTL complex. The fragment with most interactions in the binding site, F04, has been chosen as a starting point for further ligand optimization.
Looking at the resolved crystal structure of Tubulin-F04 (PDB structure 5S4O), they observed that the thiazole-amine group of F04 points toward a deep hydrophobic pocket in the αTub2 monomer that has three structural water molecules (Image 1).
Image 1: Fragment F04 co-crystallized in sID βαII binding site. The hydrophobic pocket in the αTub2 monomer with 3 structural water molecules is circled in orange. The image is prepared in the 3D Viewer of the 3decision knowledge management platform.
Interestingly, this subpocket is occupied by the phenyl moieties of the other two fragments from initial screening, F36 and F41. (PDB structures 5S5K and 5S5P, respectively) (Image 2 and 3).
Image 2: Superposition of subpocket fragments F04 (in red) and F36 (in blue).
Image 3: Superposition of F04 (in red) and F41 (in white).
The comparison was done with 3decision - a protein structure repository that allows you to easily perform 2D and 3D pocket comparisons.
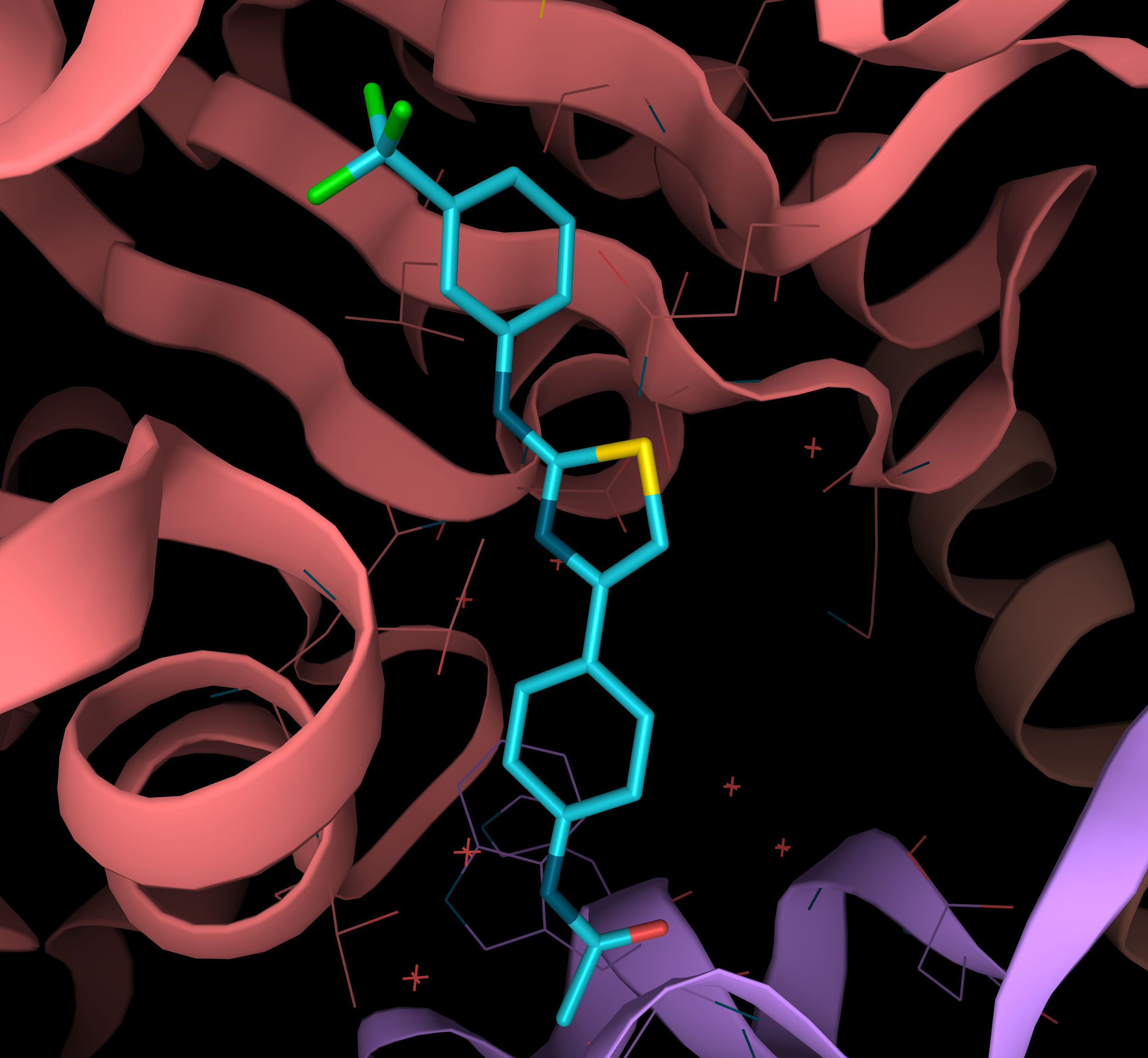
With these structural insights in mind, the researchers decided to add the phenyl substituent to the amino group of thiazole heterocycle of F04. After further optimization and characterization of fluorinated derivatives, scientists obtained Todalam – the compound that contains trifluoro-phenyl in meta-position bound to the amino group of F04 (PDB structure 5SB7) (Image 4).
In vivo and in vitro studies confirmed that this compound is the most active in inhibiting cell growth. Moreover, this compound is easy to synthesize due to its simpler chemical structure, opposite to other known antitubulin compounds.
Image 4: Todalam - a novel small molecule tubulin Inhibitor fully designed with rational structure-based approach.